PYR ( L-Pyrrolidonyl-β-Naphthylamide) Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure, Result Interpretaion, Examples and Limitation
PYR ( L-Pyrrolidonyl-β-Naphthylamide) Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure, Result Interpretaion, Examples and Limitation
PYR test is a rapid test which is used in the identification of group A beta-hemolytic Streptococci and in the differentiation of Enterococcus from group D Streptococci.
Principle
PYR test determines the activity of enzyme L-pyrroglutamyl amino-peptidase produced by Streptococcus pyogenes but not by other beta hemolytic Streptococci. L-pyrrolidonyl-β-naphthylamide (PYR) serves as a substrate for the detection of L-pyrroglutamyl amino-peptidase. The enzyme peptidase hydrolyzes the substrate PYR to produce β-naphthylamide. β-naphthylamide is detected in the presence of N, N-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde reagent by the production of bright red-colored product.
Uses/ Purpose
- This test is used to determine if the organism possesses L-prroglutamyl aminopeptidase.
- It is useful in the identification of group A beta-hemolytic Streptococci; Streptococcus pyogenes.
- It is useful in the differentiation of Enterococcus species (PYR positive) from group D Streptococci (S. bovis, S. equinus) which are PYR negative.
- It is used in the identification of Escherichia coli, separating it from other indole positive, lactose positive, gram-negative rods.
- Used to differentiate among the coagulase-negative Staphylococci.
Procedure
Here discuss two method of PYR test. These includes:
PYR Broth Assay
- Inoculate PYR broth using 3-5 colonies from a pure culture, 18-24 hours culture.
- Incubate the tube aerobically at 35-37°C for 4 hours.
- After incubation add 2-3 drops of PYR reagent to the tube.
- Observe for the red color development within 2 minutes.
PYR Disk Test
- Using sterile forceps, place PYR disk in Petri dish.
- Before inoculation, moisten disk slightly with sterile water. (NOTE: Do not flood the disc)
- Using a sterile wooden stick, pick several well-isolated colonies from 18-24 hours sheep blood agar plate.
- Gently rub a visible heavy inoculum onto a small area of PYR disc. (NOTE: False negative will occur if the inoculum is too small).
- Allow to react for 2 minute at room temperature.
- After incubation, add 1 drop of N, N-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde.
- Observe for red color development within 1 minute.
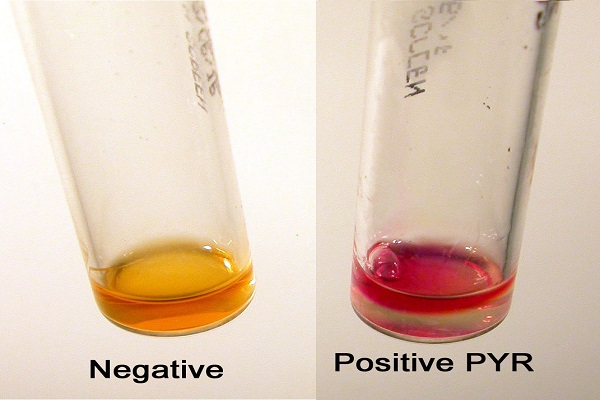
Result Interpretation
Positive: Bright pink or cherry red color development within 1 minute.
Negative: No color change.
NOTE: A pale pink reaction is considered as negative. Development of orange, salmon, yellow is interpreted as negative. (An orange color or a blue color due to a positive indole reaction)
Examples
PYR Positive Organism
Group A Streptococci (Streptococcus pyogenes), Group D Enterococci (Enterococcus), Coagulase negative Staphylococcus species such as S. hemolyticus, S. lugdunensis, S. schleiferi., Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Klebsiella, Yersinia and Serratia, Aerococcus, Gamella, Lactococcus, most Corynebacterium (Arcanobacterium) hemolyticum.
PYR Negative organism
Group B Streptococci (Streptococcus agalactiae), Streptococcus mitis, S. bovis, S. equinus, S. milleri, Escherichia coli.
Quality Control
- Perform Quality Control on each new lot of disc or color reagent with positive or negative control microorganism prior to putting into use.
- Reaction section of test strip should appear white.
- Organisms used in Quality control are:
Positive control
- Streptococcus pyogenes ATCC 19615
- Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212
- Enterobacter aerogenes ATCC 13048
Negative control
- Streptococcus agalactiae ATCC 12386
- Escherichia coli ATCC 25922
Limitation
- A false-negative result can be obtained if the disk is too moist or culture to be tested is not pure.
- Weak, pale results occur with the disk test for Staphylococcus aureus; positive results may need to be confirmed with other tests or with the tube PYR test.
- False-negative tests result if selective media or tube biochemical agars are used to provide inoculum.
- Escherichia coli and indole-positive Proteus species cultures obtained from a rich tryptophan containing media may lead blue-green color. This result concluded as a negative reaction.
PYR ( L-Pyrrolidonyl-β-Naphthylamide) Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure, Result Interpretaion, Examples and Limitation


this publication is very useful in Microbiology laboratory.