Optochin Susceptibility Test for Streptococcus pneumoniae
Optochin Susceptibility Test for Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae is found commonly in human respiratory tract, as other streptococci, and has a hemolytic pattern indistinguishable from that of other alpha-hemolytic streptococci and Lactococci.
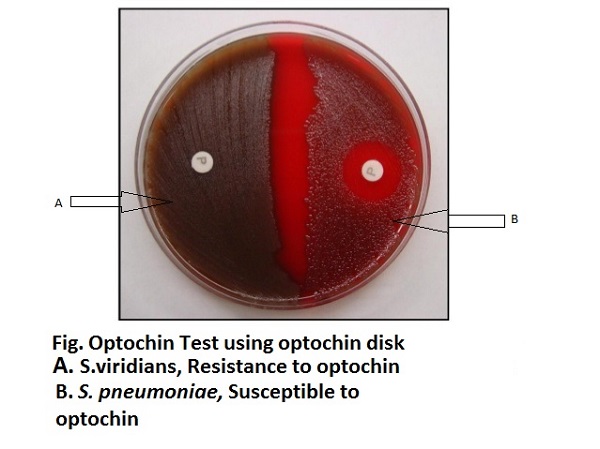
Optochin (ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) is a chemical (quinine derivative) that is used in the presumptive identification of alpha-hemolytic Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is optochin sensitive. Other alpha-hemolytic Streptococcal species are resistant to optochin. (Mnemonic: OVRPS: Optochin- Viridians Resistant and Optochin- Pneumococcus sensitive). Optochin is completely soluble in water.
The optochin test is widely used in the form of filter paper discs. In 1955 Bowen and Jeffries impregnated disks with the reagent ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride, which are applied directly to inoculated plates before incubation to demonstrate the susceptibility of pneumococcus for identification purpose.
Principle of Optochin Susceptibility Test
Optochin Susceptibility test is used to determine the effect of optochin reagent (<5 μg/ml) on an organism. This test is performed on blood agar medium using a disk diffusion principle. Optochin sensitive S. pneumoniae surrounding the disc are lysed due to the chemical optochin that changes in surface tension, resulting in zone of inhibition.
Reagents
Optochin disks- each disk is impregnated with 5µg of optochin.
5% sheep blood agar
Procedure
- Using an inoculating loop, select a well-isolated colony of the alpha-hemolytic organism to be tested.
- Streak the isolates onto 5%sheep blood agar plate.
(NOTE: Use of media other than 5% sheep blood agar is not recommended, as smaller zone sizes can result in lack of definitive identification) - Using sterile forceps, place an optochin disk onto the inoculated surface of the agar.
- Press disk gently with the sterile forceps or loop so that the disk adheres firmly to the agar surfaces.
- Incubate the plate at 35-37°C fir 18-24 hour in 5 to 10% CO2.
(NOTE: Cultures do not grow as well in ambient air, and larger zone of inhibition occur.) - Measure the diameter of zone of inhibition including diameter of disk.
Result interpretation
Sensitive: zone of inhibition ≥ 14mm (15-30mm) around the 6mm disk.
(NOTE: For 10mm disk, use ≥ 16mm zone of inhibition.
If the inhibition zone is less than 14 mm, further testing (bile solubility or serology) is indicated for the identification of S. pneumoniae.)
Intermediate: Organisms with zone of inhibiton < 14mm around the disk. The strain is identified as pneumococcus only if it is bile soluble.
Resistant: No zone of inhibition around the disk.
Quality Control
Positive: Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 49619, Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 6305
Negative: Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212, Streptococcus sanguis ATCC 15506
Limitations
- Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates should be incubated in a CO2 enriched environment, as some isolates will grow poorly or not at all.
- It has been shown that other strains of alpha-hemolytic streptococci may show a slight susceptibility to optochin.
- Optochin susceptibility is a presumptive test only. It is recommended that further biochemical tests be performed for complete identification.
- If tube bile test is performed to confirm strains with zone of inhibition between 7 and 14mm, the sensitivity in detection of nonencapsulated strains is increased; however, bile resistant strains with intermediate zone sizes may still be pneumoniae. Further testing with DNA probe is needed for definitive identification.