General Characteristics and Classification of Arthropoda
General Characteristics and Classification of Arthropoda
Arthropoda (Arthon- Jointed; podos- legs)
- Arthropoda, animals having jointed appendages or legs.
- It is a phylum of triploblastic, haemocoelomic, segmented invertebrates having head, thorax and abdomen, a chitinous exoskeleton and jointed legs and appendages.
- Most successful phylum on the Earth that has ever existed.
- Arthropods were first studied by Aristotle.
- Von Siebold coined the term Arthropoda.
General characters
- Cosmopolitan in distribution found in aquatic, terrestrial and aerial forms.
Some are ectoparasitic and vectors of disease. - Body have jointed appendages or legs (which are modified to different structures to perform different functions like jaws, gills, walking legs, paddle). There may be 3 pairs, 4 pairs, 5 pairs, many pairs.
- Body is triploblastic.
- Bilaterally symmetrical.
- Organ system level of organization.
- Body is divisible into head, thorax and abdomen.
NOTE: In some (crustacean and arachnida) body is divisible into cephalothorax (head and thorax is fused) and abdomen. - This is the first group to develop a true head, which contains sense organs and feeding organs specialized for their particular habitats.
- Body is covered with chitinous exoskeleton.
- They are haemocoelomate. Coelom i.e. body cavity is filled with blood or fluid.
- Head bears a pair of compound eyes and antenna.
- Locomotion takes place by jointed appendages.
- Digestive system is complete, straight and well developed.
The mouth bears mouth parts for ingestion of foods. Mouths are modified for chewing, biting, sponging, piercing, siphoning. - Respiration takes place by general body surface or gills (in Crustaceans) or trachea ( in insects, diplopoda and chilopoda) or booklungs (Arachnida) and book gills (in king cobra).
- Circulatory system is of open type i.e. do not have blood vessels and enters directly into the body chambers. The blood is colorless.
- Excretion takes place through Malphigian tubules (in terrestrial form) or green glands or coxal glands (in aquatic forms).
NOTE: Aquatic forms are ammonotelic, terrestrial forms are uricotelic. - Nervous system is of annelidian type, which consists of brain and ventral nerve cord.
- Unisexual i.e. sexes are separate.
- Fertilization is internal or external.
- They are either oviparous or ovoviviparous.
- Development may be direct or indirect.
- Sensory organ include antennae, sensory hairs for touch and chemoreceptor, simple and compound eyes, auditory organs (in insects) and statocysts (in crustacean).
Examples
| Zoological name | Common name |
| Limulus | Horse shoe crab or King crab |
| Daphnia | Water flea |
| Cancer | Crab |
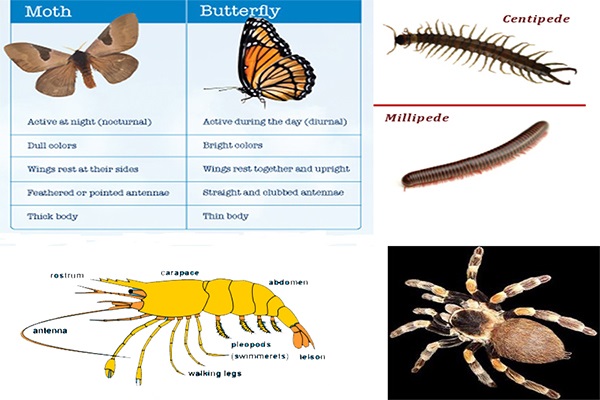
| palaemon | Prawn |
| Astacus | Cray fish |
| Scolopendra | Centipede |
| Julus | Millipede |
| Aranea | Spider |
| Periplaneta americana | Cockroach |
| Bombyx | Moth |
| Pieris | Butterfly |
| Musca | Housefly |
| Apis | Honeybee |
| Melanopus | Grasshopper |
| Palamnaeus | Scorpion |
Insects as disease carriers
| Insects | Disease |
| Housefly | Typhoid, Cholera, Dysentry, Diarrhoea |
| Mosquitoes | Malaria, Filariasis, Encephalitis, Dengue fever |
| Kissing bug | Chaga’s disease |
| Rat flea | Bubonic plaque. |
| Sand fly | Kala-azar |
| Bed bug | Typhus fever |
| Tsetse fly | African sleeping sickness |
| Body louse | Relapsing fever |
Classification
On the basis of jointed appendages, arthropods are classified into following classes:
| Character | Crustacean | Myriapoda | Arachnida | Insect |
| Habitat | Mainly aquatic, few live in moist place.Few are parasitic form | Terrestrial, found under logs of wood stones etc. | Terrestrial. Some are parasitic. | Terrestrial and rarely aquatic. Some are parasitic. |
| Appendages/ walking legs | Five pairs | Many pairs | Four pairs | Three pairs. |
| Division of body | Cephalothorax and abdomen. | Head, thorax and abdomen. | Cephalothorax (prosome) and abdomen (opisthosoma) | Head, thorax and abdomen. |
| Antenna | Two pairs | One pair | No antenna | One pair |
| Respiration takes place by | Gills | Trachea | Trachea and book lungs | Trachea |
| Eye | Compound eye | Compound eye | Distinct eye | Compound eye |
| Excretion | Coxal gland or Green gland or Antennary | Malpighian tubules | Green gland | Malpighian tubules |
| Examples | Prawn | Millipede | Spider, Scorpion | Butterfly, Moth |
Things to Remember
- Largest phylum in the animal kingdom.
- Body is covered by chitinous exoskeleton which undergoes periodical ecdysis. The process of casting off of skin or integument is called ecdysis or moulting.
- Cuticle is secreted by epidermis of skin. It protects the internal organs and provides space for the attachment of muscles.
- Spider produces web by means of spinnerets.
- Scorpion produces toxin by means of telson (tail).
- In prawn, only oxygenated blood flows.
- Prawn has 19 pairs of appendages.
- Larva of cockroach is called Nymph.
- In cockroach heart is thirteen chambered.
- Female cockroach lack anal style. Whereas male cockroach are stylish.
- Cockroach receives ultrasonic sound by means of anal circuit.
- Mouth parts adapted for various modes of feeding in Arthropods are:
- Biting and chewing type: Cockroach, grasshoppers
- Chewing and lapping type: bees and wasps
- Piercing and sucking type: Bugs, Aphids, Mosquitoes
- Sponging type: Housefly
- Siphoning type: Butterflies and moth
- Haemoglobin absent in blood so called haemolymph.
- Periplatus is a connecting link between Annelida and Arthropoda.
General Characteristics and Classification of Arthropoda
(Visited 230,797 times)

I was honored to get a call from a friend as soon as
he discovered the important ideas shared on your
site. Examining your blog write-up is a real great experience.
Thank you for taking into consideration readers like me, and I desire for you
the best of success like a professional in this arena.
you have covinced me
Thanks
If love this
the site is soo amazing. Bravoooooh!!!!!!!!!!
Thnx
Really helpful..
some special
Amazing 😍😍😍😍😍
Nyc
loved it
Really helpful
Well understanding I love it so and also plz explain briefly about any context. thanks it’s helpful for me.
Thanks.. For the information about Arthropoda
Wow wonderful site