Bacitracin Test- Principle, Procedure, Result with Limitation
Bacitracin Test- Principle, Procedure, Result with Limitation
Bacitracin is produced by Bacillus licheniformis and it interrupt the formation of peptidoglycan, a major component of bacterial cell wall. If bacitracin is present it blocks bactoprenol from transporting NAM and NAG sugars across the cell membrane thereby inhibiting further synthesis of peptidoglycan.
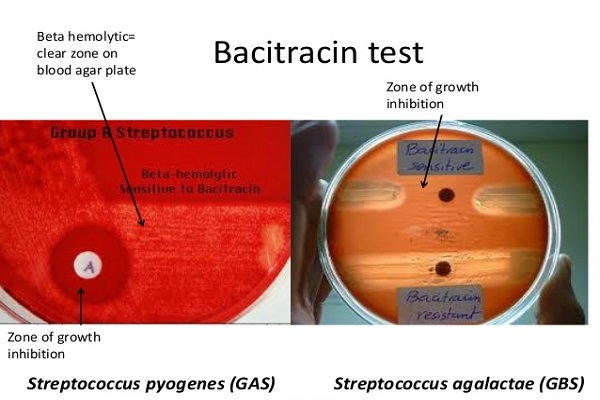
The presumptive identification of beta hemolytic Group A streptococci from beta hemolytic non-Group A Streptococci is usually done by testing for sensitivity to bacitracin. Many laboratories use this test as the sole test for diagnosing GAS infections due to the difficulty in performing sero-grouping and high cost of antisera. This test determines whether the bacterium is either sensitive (susceptible) or resistant to bacitracin.
Principle
The bacitracin susceptibility test is used to distinguish Group A streptococci, from other streptococci. This test is used to determine the effect of small amount of bacitracin (0.04U) on an organism. Sterptococcus pyogenes is inhibited by the small amount of bacitracin in the disk; other beta-hemolytic streptococci usually or not.
Procedure
- With a sterile inoculating loop, select 2-3 well isolated colonies of suspected beta-hemolytic organism from an 18-24 hours old culture.
- Streak the colonies onto a blood agar plate.
- Using heated forceps, place a bacitracin disk in the first quadrant (area of heaviest growth). Tap the disk with forceps to ensure adequate adherence with the agar surface.
- Incubate the plate in ambient air at 35°C-37°C for 18-24 hours.
- After incubation, observe the zone of inhibition around the bacitracin disk.
Results
Positive: Any zone of inhibition around the disk.
Examples: Streptococcus pyogenes
Negative: No zone of inhibition.
Example: streptococcus agalactiae
Quality control
Positive: Streptococcus pyogenes ATCC 19615
Negative: streptococcus agalactiae ATCC 13813
Limitation
- An old dried out blood agar plate should not be used because it reduces diffusion of the bacitracin giving a false-negative result.
- Due to differences in zone size resulting from different concentrations of bacitracin, differential disk (0.04 units) in comparison to sensitivity disks (10unites), are used in the test.
- When testing isolates, a light inoculum may result in false zone of inhibition. So it is important that an inoculum resulting in confluent growth be used.
- It is recommended that biochemical and/or serological tests such as latex agglutination can be performed on colonies from pure culture for complete identification.

thank you your paged help me in making my assignment.
THANK YOU