External and Internal Features of Paramecium caudatum
External and Internal Features of Paramecium caudatum
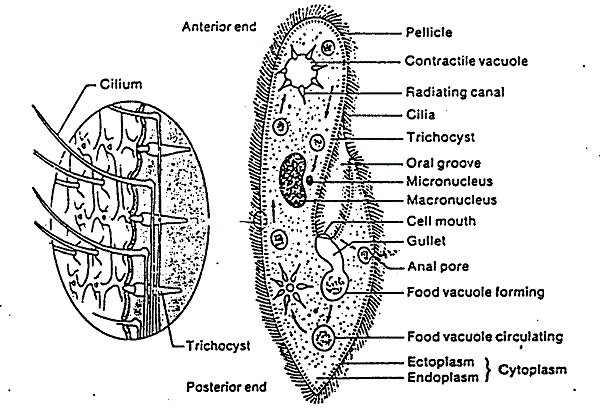
External features of Paramecium
1. Shape: Paramecium is lengthy and resembles like the sole of slipper or shoe. Hence commonly called slippper animalcule. Its body has rounded anterior end and conical or slightly pointed end.
2. Size: Varies in size from 0.15-0.3 mm in length and 0.045-0.07 mm in width.
3. Pellicle: It is the covering of paramecium. It is thin, tough, elastic and colorless membrane. Because of the presence of pellicle, Paramecium always maintains its shape and also protects the internal organelles from mechanical injuries.
4. Cilia: They are tiny hair like projections distributed throughout the body. Paramecium contains 10000-14000 cilia. There are two types of cilia present in paramecium. They are oral cilia and body cilia.
Oral cilia are present in vestibule and oral groove. They helps in collection of food materials.
Body cilia are found in the body surface and helps in locomotion. They are of moderate and fairly uniform in length but at the posterior end, cilia are quite longer called caudal tuft.
5. Oral groove and cytoproct:
Oral groove is large oblique pocket like depression. It is situated in ventrolateral surface. It drives food materials. Oral groove leads into v-shaped cavity called vestibule. Vestibule leads into oval shaped opening called cytosome. Cytosome leads into funnel shaped cytopharynx.
NOTE: Due to oblique position of oral groove the organism has lost its symmetry.
Cytoproct is small opening present on the ventral surface just behind the cytopharynx. From this opening, undigested food materials are passed outside the body. So it is called cell anus.
Internal Structures of Paramecium
Internal structures of Paramecium consists of cytoplasm, trichocysts, food vacuoles contractile vacuoles etc.
1.Cytoplasm: is differentiated into two types i.e. ectoplasm and endoplasm.
a. Ectoplasm: It is a thin clear transparent outer layer. It consists of trichocysts, cilia and pellicle.
Trichocysts: These are small oval or spindle shaped structure situated in the ectoplasm. These are numerous and tiny structures. These are opened outside through a minute pore on the pellicle surface. The trichocysts are discharged on mechanical, chemical or electric stimuli. After they are discharged, new ones are generated from kinetosomes.
Function: It helps in offence, defense and adhesions. Also helps to form endoskeleton or supports the body.
b. Endoplasm: Endoplasm of Paramecium is more fluid and voluminous thick granular part of the cytoplasm. It contains two nucleus, numerous food vacuoles and contractile vacuoles.
i. Nucleus:
Paramecium has two nuclei, one macronucleus or mega nucleus and other micronucleus. These nuclei are not only differ in shape and size but also in function.
Meganucleus or macronucleus: It is large kidney shaped in structure, located in the middle dorsal part of the body opposite to cytopharynx. Nuclear membrane is absent in it. It divides asexually during reproduction. During transverse binary fission it divides amitotically.
It is vegetative in function i.e. controls all the metabolic activities of the organism.
Micronucleus: It is small spherical or rounded in structure. It is situated in the depression of macronucleus. It divides mitotically during transverse binary fission. During conjugation reproduction, it divides first meiotically then mitotically.
It controls the process of sexual reproduction but fails to reproduce.
NOTE: Paramecium also survive without micronucleus but fails to reproduce.
ii. Contractile vacuoles: There are two types of contractile vacuoles present in paramecium. It is located in the dorsal surface of anterior and posterior end.
Each contractile vacuole is connected to 8/10 radial canals.
The two contractile vacuoles work alternatively, but posterior vacuole contracts more rapidly than anterior contractile vacuole because it is near to cytopharynx and more water comes into it.
The main function: helps in the removal of carbondioxide and other metabolic waste products to outside. And also maintains the osmoregulation.
iii. Food vacuoles: numerous non- contractile vacuoles present in paramecium called food vacuoles or gastrioles. Its shape and size changes according to the quality of food particles.

Wow……….wonderful post.helped me a lot.
I love this. thanks
Niçe…….,