Feeding Mechanism in Paramecium
Feeding Mechanism in Paramecium
Paramecium feeds holozoically with the help of cilium.
Food includes bacteria, unicellular plants (algae, diatoms, yeasts, etc.) and small bits of animal and vegetables.
Paramecium swims to place where it can get its food. It does not move while feeding.
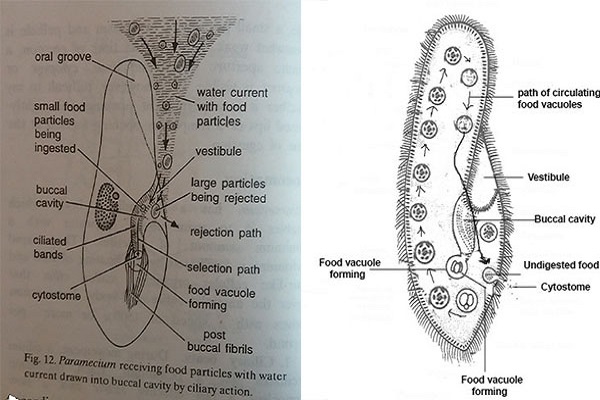
Food is ingested by cytosome lying at the bottom of buccal cavity. At first cilia of oral groove move very fast that drives current of water with food particles toward vestibule. Ciliary tracts of vestibule direct the food particles into buccal cavity. Larger food materials are rejected whereas smaller food materials are selected and ingested through cytosome into cytopharynx. The food now gradually collects at the bottom of cytopharynx into a membranous vesicle which is later released off as food vacuole.
Digestion: Each food vacuole consists of food particles and it undergoes circulation in definite path along with cyclosis. Digestion takes place with the help of certain enzymes secreted by protoplasm into the vacuoles. The contents of vacuole first become acidic and then become alkaline. The major digestion of food occurs during the alkaline phase. In digestion proteins are converted into aminoacids, carbohydrates into soluble sugar and glycogen. Products of digestion are diffused into the surrounding cytoplasm and either stored or used for vital activity and growth.
Finally the undigested food materials is eliminated from the body through anal spot or cytoproct on ventral surface.

Liked it . really helped me