General Description of Paramecium
General Description of Paramecium
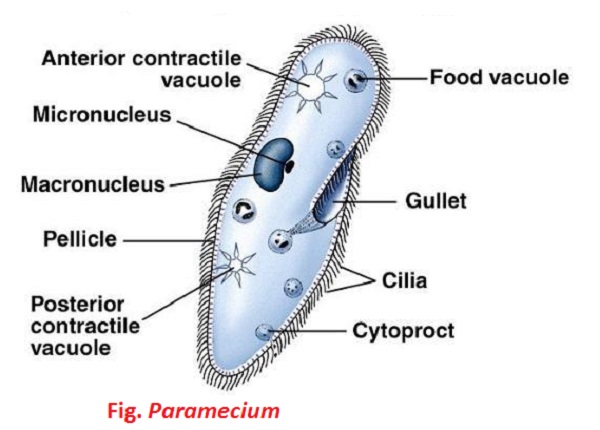
Paramecium is a unicellular, microscopic, free-living organisms. It is the most common ciliates, characterized by the presence of cilia, nuclear dimorphism and unique type of sexual reproduction (conjugation).
History
- Paramecium was named by John Hill in 1752.
- Antony van Leeuwenhoek described about paramecium.
Different species of paramecium are grouped into two categories
| Aurelia group | Bursaria group |
| Are elongated, spindle shaped body. | Short and broad, posterior end is somewhat broad. |
| Length more than width. | |
| Cytoproct is lateral. | Cytoproct is sub-terminal. |
| e.g. P.caudatum, P.aurelia | e.g. P. bursaria, P.trichium |
What is its common name? Why is it called so?
Its common name is slipper animalcule. It is called so because it looks like the sole of shoe or slipper.
NOTE: Louis Joblot gave the name chausson or slipper and the phrase slipper animalcule remained in used.
Paramecium caudatum
Systemic position
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Protozoa
Subphylum: Ciliophora
Class: Ciliata
Genus: Paramecium
Species: caudatum
Why the species name given caudatum?
Due to the presence of caudal tuft in the posterior region it is called caudatum.
Paramecium caudatum is also called infusorian animalcule because it is found in place where decaying or decomposed organic matter and bacteria are found.
General characters
- Occurrence: It is found in freshwater ponds, pools, ditches, streams, rivers, lakes, etc. It is abundantly found in stagnant water, where decaying organic matter is in plenty.
- Locomotion: It moves here and there with the help of cilia, which also functions as food capture.
- Nutrition: It ingests bacteria and other microscopic organisms or minute protozoans. So nutrition is holozoic.
- Digestion: intracellular.
- Respiration and excretion: takes place by general body surface through diffusion process.
In paramecium, excretion is also done contractile vacuole and cytoproct. - Reproduction: Asexually by transverse binary fission and sexually by conjugation.
What is cyclosis?
Streaming movement of food vacuoles along with endoplasm is known as cyclosis. During cyclosis food is digested completely. So digestion is intracellular.

Best note
The best notes help a lot……..
Good
thank