Mechanism of Breathing
Mechanism of Breathing
Breathing is simply defined as the physical process in which oxygen is taken into the body and carbon dioxide is forced out from the body.
Breathing is brought about by two sets of muscles-
i. Internal intercoastal muscles
ii. External intercoastal muscles
Besides these muscles, diaphragm and abdominal muscles help in breathing.
The process of breathing involves two phases:
- Inspiration/ Inhalation
- Expiration/ Exhalation
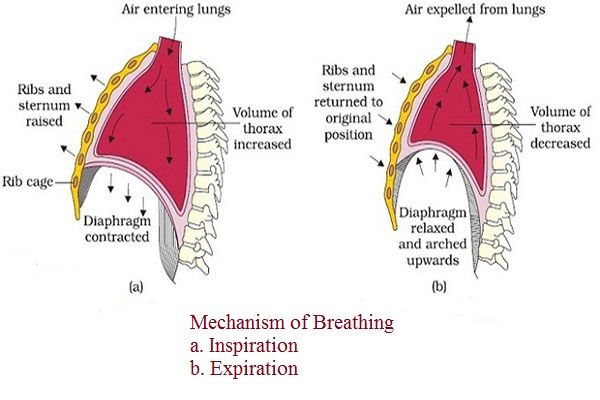
1. Inspiration
It is the inhalation of air into lung and is brought about by chest expanding.
It takes place when the volume of thoracic cavity increases and the air pressure decreases.
Enlargement of thoracic cavity involves the following events which occurs simultaneously:
- During inspiration, the external intercostal muscles contract and the internal one relax.
- Due to contraction of external intercostal muscles, the ribs are pulled upward and outward.
- The muscle of diaphragm contract which lowers the diaphragm.
- As a result the size of thoracic cavity increases as well as the lungs expand simultaneously.
- As the lungs expand, the air pressure inside the lungs decreases.
- In order to balance the air pressure, air rushes from atmosphere into the lungs through air passage.
The process of inspiration is active, as it needs energy for muscle contraction. At rest, it lasts about 2 sec.
 2. Expiration
2. Expiration
It is the forcing of air out from lungs and is brought about by chest contracting.
It takes place when the size of thoracic cavity is reduced and the air pressure is increased.
The process involves in expiration are as follows:
- The internal intercostal muscle contract.
- Due to contraction of internal intercostal muscles, ribs are pulled back to their normal position.
- The muscle of diaphragm relaxes and comes to its original dome-shaped.
- As a result, the size of thoracic cavity decreases and the size of lungs also decreases.
- Due to which the air pressure increases in lungs.
- In order to equalize the air pressure, air is expelled out from the lungs to the atmosphere through respiratory tract.
Expiration is passive process as it does not require the expenditure of energy.

Good explanation
thank you
good explanation, but what exactly are the mechanism of breathing? Is it the various muscles, ribs….
Very useful, thanks.
Good and precise but what are intercoastal muscles?
intercoastal muscles are the muscles which is between rib cages
Very …nice …explaination
Very nice explanation
good one bro.Easy to understand the points .
Awesome …….. Thank you very much for information…..
Thanks
Very nice explanation!
good explanation! thanks
Very simplified and easily understanderble mechanism of external respiration
Well summerised and interpreted thanks job weldone.
A very good clear explanation. Thanks
Well organised
thanks
Good.very simple and neat explanation.
Very good explanation
Thanks for the genuine answer, it ease my understanding